OSPFv3 Important Points
OSPFv3 is a link-state protocol for IPv6. A link-state protocol makes its routing decisions based on the states of the links that connect source and destination machines. The state of a link is a description of that interface and its relationship to its neighboring networking devices. The interface information includes the IPv6 prefix of the interface, the network mask, the type of network it is connected to, the devices connected to that network, and so on. This information is propagated in various type of link-state advertisements (LSAs).
OSPFv3 is similar to OSPFv2 in its concept of a link state database, intra-
and inter-area, and AS external routes and virtual links. It differs
from its IPv4 counterpart in a number of respects. In OSPFv3, peering is done through link-local addresses and the protocol is
link based rather than network based. Also, the addressing semantics have
been moved to leaf LSAs, which eventually allow its use for both IPv4
and IPv6. Point-to-point links are also supported in order to enable
operation over tunnels. It is possible to enable OSPF and OSPFv3 at the
same time. OSPF works with IPv4, and OSPFv3 works with IPv6. Unlike OSPF version 2, multiple instances of OSPFv3 can be run on a link.
Some key featues of OSPFv3 are listed below:
- OSPFv3 is described in RFC 2740.
- OSPFv3 can form adjacencies with neighbor routers that are not on the same subnet.
- Multiple instances of OSPFv3 can run on each link.
- OSPFv3 can run concurrently with OSPFv2 because each version maintains its own database and runs a separate SPF calculation.
- Administrative distance (AD) and Metric, Hello (10Sec), hold down time (40 sec) parameters, DR/BDR election for the shared network, link-types, Functionality of Hell, DBD, LSR, LSU, Link State Ack packets remain same.
- In OSPFv3 Area ID, router ID, and link-state ID are defined as 32-bit fields.
- Multicast address used by OSPFv3 is FF02::5 & FF02::6. Hello messages are sent at FF02::5.
- OSPFv3 uses link-local address that enables a node to communicate with other nodes on the link.
- Authentication is no longer built-in but relies on the underlying capabilities of IPv6. OSPFv3 uses the IPv6 Authentication Header and Encapsulating Security Payload for security.
- IPv6 unicast-routing is not enabled by default and must be configured specifically in global config mode.
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)# ipv6 router ospf process-id
R1(config-rtr)# router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config)# interface f0/0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
The above command will not be accepted if "ipv6 unicast-routing" is not configured.
R1(config)# interface f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
% OSPFv3: IPv6 routing not enabled
O 2001:10:10::2/128 [110/1] via FE80::C802:27FF:FE5C:0, FastEthernet0/0
R1#show ipv6 ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area Intf ID Cost State Nbrs F/C
Lo0 10 0 21 1 LOOP 0/0
Fa0/0 10 0 2 1 DR 1/1
R1#sh ipv6 OSPF neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 10)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:31 2 FastEthernet0/0
R1#sh ipv6 OSPF neighbor detail
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 10)
Neighbor 2.2.2.2
In the area 0 via interface FastEthernet0/0
Neighbor: interface-id 2, link-local address FE80::C802:27FF:FE5C:0
Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL, 6 state changes
DR is 1.1.1.1 BDR is 2.2.2.2
Options is 0x000013 in Hello (V6-Bit, E-Bit, R-bit)
Options is 0x000013 in DBD (V6-Bit, E-Bit, R-bit)
Dead timer due in 00:00:31
Neighbor is up for 00:55:26
Index 1/1/1, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
- Configuring OSPFv3
R1(config)# ipv6 router ospf process-id
R1(config-rtr)# router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config)# interface f0/0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
The above command will not be accepted if "ipv6 unicast-routing" is not configured.
R1(config)# interface f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
% OSPFv3: IPv6 routing not enabled
- Few more useful commands:
O 2001:10:10::2/128 [110/1] via FE80::C802:27FF:FE5C:0, FastEthernet0/0
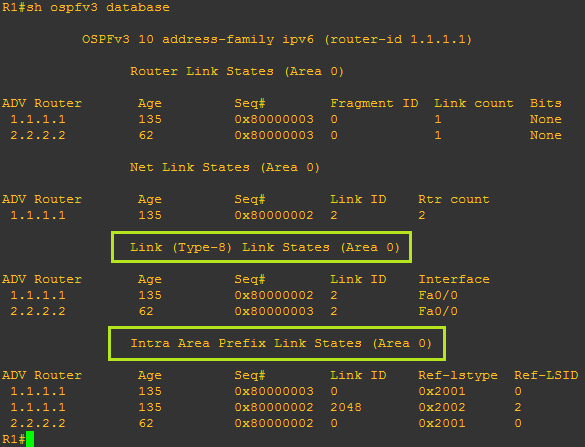
- You can check OSPFv3 Database using "show ospfv3 database" command. Two new LSA types have been added in OSPFv3. Link LSA and Intra Area Prefix Link States LSA.
- Advertising the link-local address to all routers that are attached to the link.
- Advertising IPv6 prefixes on the link to the routers that are attached to the link.
- Advertising options (Example: V6 Bit).
- Command to check: show ipv6 OSPF 1 database link.
- Associating a list of IPv6 prefixes with a transit network by referencing a network LSA.
- Associating a list of IPv6 prefixes with a router by referencing a router LSA.
- Command to check: show ipv6 OSPF 1 database prefix.
R1#show ipv6 ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area Intf ID Cost State Nbrs F/C
Lo0 10 0 21 1 LOOP 0/0
Fa0/0 10 0 2 1 DR 1/1
R1#sh ipv6 OSPF neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 10)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:31 2 FastEthernet0/0
R1#sh ipv6 OSPF neighbor detail
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 10)
Neighbor 2.2.2.2
In the area 0 via interface FastEthernet0/0
Neighbor: interface-id 2, link-local address FE80::C802:27FF:FE5C:0
Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL, 6 state changes
DR is 1.1.1.1 BDR is 2.2.2.2
Options is 0x000013 in Hello (V6-Bit, E-Bit, R-bit)
Options is 0x000013 in DBD (V6-Bit, E-Bit, R-bit)
Dead timer due in 00:00:31
Neighbor is up for 00:55:26
Index 1/1/1, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
If you like this article, kindly share the same with your friends.