Routing Information Protocol - RIP
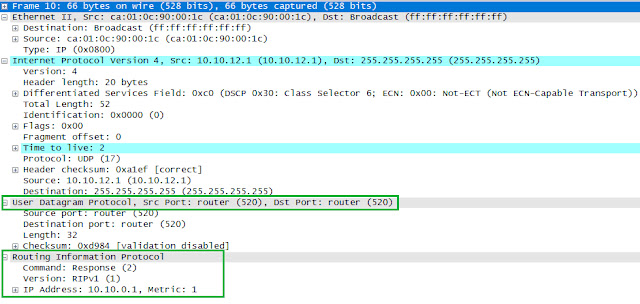
Routing Information Protocol - RIP is an Interior Gateway Protocol that is designed to support routing in small private networks. It is an Application layer protocol that runs on top of UDP well-known port 520.
Routing Information Protocol Versions
Routing Information Protocol operates using two versions: RIP Version1 and RIP Version2
Routing Information Protocol Protocol Type
Distance Vector. The term 'Distance' means how many hops away the destination subnet is located and 'Vector' is technical name for direction, means, through which next-hop or exit interface the destination prefix is located.
Routing Information Protocol Default AD
RIP has default AD value of 120 (for both version 1 and version 2). Can be changed using "distance x" router configuration command.
Routing Information Protocol Mertic
RIP considers Hop Count as its metric. Maximum Hop count allowed is 15. A destination that is 16 hops away is considered unreachable. RIP prevents routing loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination. Routing Information Protocol Algorithm
RIP uses Bellman-Ford algorithm to compute the metric.
Routing Information Protocol Timers
RIP does not have any way of reliability therefore the updates are sent
periodically every 30 seconds. RIPv1 Broadcast address are used at both Layer 2
(FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) and Layer 3 (255.255.255.255). RIPv2 uses Multicast addresses at both Layer 2 (01:00:5e:00:00:09) and Layer 3(224.0.0.9). Below is brief description of RIP timers. Kindly read the article RIP Timers for more details.
- Update: The time between each update interval. This value is set to 30 seconds, by default, and is configurable.
- Invalid: The time after which a suspect route becomes invalid. This is set to 180 seconds, by default.
- Hold-down: The time used to suppress the possibility of defective routes being installed in the routing table. The default time is 180 seconds.
- Flush: The time after which a route is removed from the routing table. This is set to 240 seconds, by default.
Routing Information Protocol Authentication
RIPv1 does not support Authentication. Only RIPv2 supports Authentication.
A router can be configured to run RIPv1 as well as RIPv2 at same time. In a topology R1--R2--R3, R2 is running RIPv2, however, it can also be configured to run RIPv1 with R1(if R1 doesn't support v2 due to IOS constraints) and R2 can run RIPv2 with R3. Below is interface level command where R2 is configured to run Version1 with R1 (R2's f1/0 is interface connected to R1).
R2(config-router)#int f1/0
R2(config-if)#ip rip send version 1
R2(config-if)#ip rip send version 1
Routing Information Protocol Commands
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 27 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive version 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
FastEthernet1/0 1 2
FastEthernet1/1 2 2
Loopback0 2 2
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.10.12.1 120 00:02:38
10.10.23.3 120 00:00:09
Distance: (default is 120)
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 27 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive version 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
FastEthernet1/0 1 2
FastEthernet1/1 2 2
Loopback0 2 2
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.10.12.1 120 00:02:38
10.10.23.3 120 00:00:09
Distance: (default is 120)
RIP stores all the updates received its peers first in the database (control plane). The best routes from the database are moved to the routing table.
R2#show ip rip database
10.0.0.0/8 auto-summary
10.10.0.0/24 directly connected, Loopback0
10.10.0.1/32
[1] via 10.10.12.1, 00:00:19, FastEthernet1/0
10.10.12.0/24 directly connected, FastEthernet1/0
10.10.23.0/24 directly connected, FastEthernet1/1
10.0.0.0/8 auto-summary
10.10.0.0/24 directly connected, Loopback0
10.10.0.1/32
[1] via 10.10.12.1, 00:00:19, FastEthernet1/0
10.10.12.0/24 directly connected, FastEthernet1/0
10.10.23.0/24 directly connected, FastEthernet1/1
R2#Show ip route rip
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
R 10.10.25.0/24 [120/1] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:05, FastEthernet1/0
R 10.10.35.0/24 [120/2] via 10.10.14.4, 00:00:06, FastEthernet2/0
192.9.1.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 192.9.1.5 [120/2] via 10.10.14.4, 00:00:06, FastEthernet2/0
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
R 10.10.25.0/24 [120/1] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:05, FastEthernet1/0
R 10.10.35.0/24 [120/2] via 10.10.14.4, 00:00:06, FastEthernet2/0
192.9.1.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 192.9.1.5 [120/2] via 10.10.14.4, 00:00:06, FastEthernet2/0
RIP routes are denoted by 'R' in the Routing table.
We can also use RIP debugging for troubleshooting routing issues related to RIP.
R1#debug ip rip
RIP protocol debugging is on
R1#
*Sep 3 20:31:09.755: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet2/0 (10.10.14.1)
*Sep 3 20:31:09.759: RIP: build update entries
*Sep 3 20:31:09.763: 10.10.12.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
*Sep 3 20:31:09.767: 10.10.13.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
*Sep 3 20:31:09.767: 10.10.25.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0
R1#
RIP protocol debugging is on
R1#
*Sep 3 20:31:09.755: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet2/0 (10.10.14.1)
*Sep 3 20:31:09.759: RIP: build update entries
*Sep 3 20:31:09.763: 10.10.12.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
*Sep 3 20:31:09.767: 10.10.13.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
*Sep 3 20:31:09.767: 10.10.25.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0
R1#
I hope you have found this article informative and useful and now have a fair understanding of Routing Information Protocol - RIP Characteristics. For any of the related queries or feedback, kindly write to us at networkurge@gmail.com






0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.